LEARNING DISABILITIES
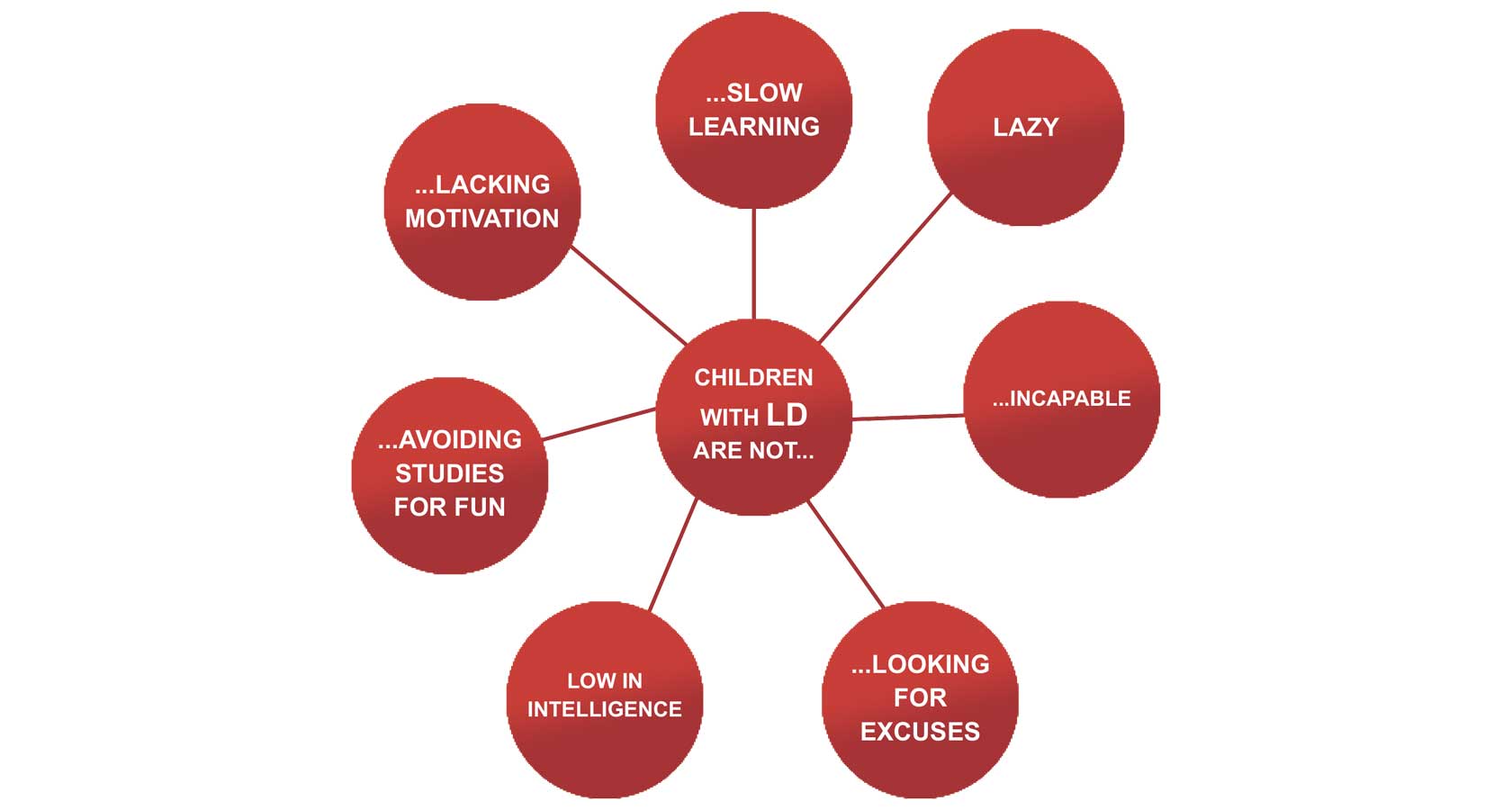
Learning Disabilities (LD) is a collective term for a wide variety of learning problems. Learning disabilities are problems that affect the brain's ability to receive, process, analyze, or store information. Children and adults with learning disabilities see, hear, and understand things differently. This can lead to problems with learning new information and skills, and putting them to use. This could lead to underachievement, which is unexpected based on the child's potential as well as the opportunity given to have learned more.
The most common types of learning disabilities involve problems with reading, writing, math, reasoning, listening, and speaking. COMMON TYPES OF LEARNING DISABILITIES Dyslexia – Difculty with reading
- Difficulty understanding the relationship between sounds, letters and words
- An inability to grasp the meaning of words, phrases, and paragraphs
- Letter and word recognition could be difficult
- Understanding words and ideas may not be easy
- Reading speed and fluency is slow
- General vocabulary skills is low
Dyscalculia – Difficulty with math
- Difficulty learning and remembering numerals
- Cannot remember basic facts about numbers
- Slow and inaccurate in computation
- Difficulty in understanding mathematical terms
- Difficulty in converting written problems into mathematical symbols
- The ability to recognize and understand symbols
- Difficulty with basic addition, subtraction, multiplication, division an following sequences of basic operation
Dysgraphia – Difficulty with writing
- Poor spellings – phonetic error (an erroneous spelling that sounds like the correct spelling)
- Errors in grammar and punctuation
- Poor handwriting
- Difficulty in organizing thoughts on paper
- Physical difficulty forming words and letters
- Problems with neatness and consistency of writing
- Inaccurately copying letters and words
- Issues with writing organization and coherence
OTHER TYPES
Dyspraxia – Difficulty with fine motor skills
- Problems with movement - Issues with hand-eye coordination
- Perception problems
Dysphasia – Difficulty with language
- Inability to understand or produce spoken language
- Struggling to find the appropriate term or word
- Difficulty in comprehension - Language delay
Auditory Processing Disorder – Difficulty hearing differences between sounds
- An inability to distinguish subtle differences in sound
- Poor auditory attention and auditory memory
- Often misunderstands what is said, needs information to be repeated
- Poor expressive language skills
- Find it hard to follow spoken directions, especially multi-step instructions
Visual Processing Disorder – Difficulty interpreting visual information
- Difficulty in identifying differences in shapes
- Reversing letters or numbers
- Skipping words and lines
- Difficulties with perceiving depth or distance
COMORBIDITY WITH LEARNING DISABILITIES
Comorbidity is described as a situation where two or more conditions that are diagnostically distinguishable from one another tend to occur together. Learning disabilities is very often confused with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). It is important to understand that these are two separate conditions, irrespective of the significant level of co-morbidity. A child with one type of disability could also be diagnosed with another type together. For example: A child can have Dyslexia and Dysgraphia together. Alot of children with ADHD can also have a learning disability. Depression and Anxiety are also possible comorbid disorders. Look out for the next article for more on Learning Disabilities.
Recent Articles
- Aptitude, Interest, Personality for Career
- Careers and Their Pathways
- Depression Need Not Be A Lifestyle
- Exams = Tension, Worry, Stress, Anxiety, Fear?
- Healthy Body + Healthy Mind = Healthy Life
- Learning Disabilities-Part 2
- Quit Tobacco Today!
- Stress Management
- The Two Poles of Mood:Bipolar Disorder
- Understand The World of Adhd!!!
- What is Schizophrenia
- Youth and Mental Health